Islamic Architecture and Its Global Influence
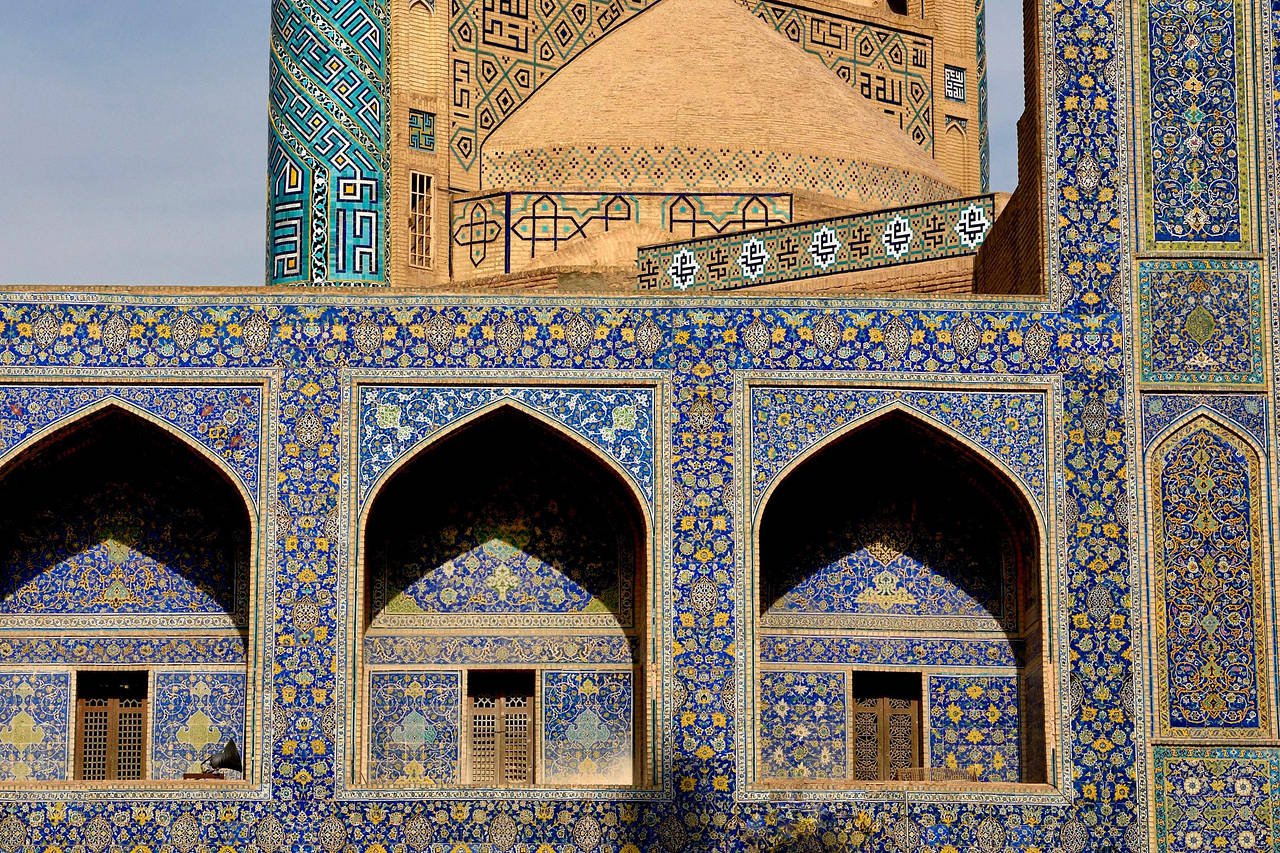

Table of Contents
“At the height of Islamic civilisations came a magnificent flowering of the arts and architecture: the buildings created by the great Islamic dynasties rank among the finest monuments of world culture. To focus one’s attention on material details of these creations and on their representation in the pictorial arts of the time makes one understand better how they reflect the all-encompassing unity of man and nature, central to Muslim belief.”
– Mawlana Hazar Imam, Introduction to “Architecture in Islamic Arts,” Aga Khan Trust for Culture, July 2012
Islamic architecture, with its dazzling geometric patterns, soaring domes, and majestic pointed arches, has enchanted the world for centuries. This distinctive form of art has left an indelible mark on Islamic architecture history with its radiant colours, symmetrical silhouettes, and intricate designs. It is a style that has captured the hearts of many, both near and far.
While Islamic architecture is most commonly associated with Arab states and Muslim-majority countries, its influence has spread across the globe, even reaching European nations with Arab or Islamic histories. Indeed, the universal appeal of this style lies in its ability to transcend borders and cultures.
In this blog, we will explore the history, styles, and Islamic architecture elements that have garnered admiration and led to its profound influence on cultures across the world.
Also read: How Is Computational Design Used in Architecture in 2023?
The Advent of Islamic Architecture
The 7th century CE marked a turning point in the Islamic architecture history of the Arabian Peninsula, with the emergence of a religion that would come to shape the region’s artistic and cultural traditions. Born in the bustling city of Mecca (Makkah), Islam was founded by a merchant named Muhammad. As Muhammad's teachings began to spread throughout the Middle East, North Africa, and Southern Europe, the impact of this new religion was profound. Islamic culture began to flourish, with centres of learning emerging across the region, devoted to subjects ranging from philosophy and astronomy to medicine and the arts. But it was in the realm of architecture that the influence of Islam was perhaps most keenly felt.
.jpg?width=1440&height=885&name=An%20illustration%20of%20the%20city%20of%20Makkah%20(Mecca).jpg)
The emergence of Islamic architecture was inextricably linked to the rise of Islam itself. The first mosques were simple structures, typically consisting of a courtyard surrounded by a portico, intended as community centres rather than grand edifices. Yet, as Islam spread, so did the sophistication and ambition of its architecture.
One of the key influences on Islamic architecture was the pre-Islamic architectural traditions of the region, which included the Byzantine, Sassanian, and Roman styles. Islamic architects drew upon these traditions, as well as the decorative motifs of Central Asia and the geometric patterns of the Persian Empire, to create a distinctive and unified style.
The earliest surviving example of Islamic architecture is the Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem, which was built in 691 CE by the Umayyad Caliph Abd al-Malik. The building's circular plan and soaring dome were inspired by Byzantine models, while its intricate mosaics and calligraphic inscriptions were uniquely Islamic.

Also Read: 8 Best Places to Learn Computational Design (2023)
History of Islamic Architecture
The provinces where Islamic architecture first emerged were centred around the Arabian Peninsula, with cities such as Medina and Mecca serving as the initial sites of Islamic architecture. Over the centuries, Islamic architecture concepts have expanded beyond its religious context, with Islamic architecture influences from local styles and cultural traditions melding with the core Islamic aesthetic.
In the 8th and 9th centuries, the Islamic empire spread across North Africa and into Spain, with cities like Cordoba and Granada becoming centres of Islamic architecture. The iconic Mezquita in Cordoba, for instance, with its horseshoe arches, intricate tilework, and ornate decoration, is a testament not only to Islamic presence but also to tolerance and diversity in the region. Features of Islamic architecture include carvings and arches that coexist with Roman columns, prehistoric stone walls, possibly Gothic ornamentation, and a Renaissance bell tower in the Mezquita.

In the 10th and 11th centuries, the Fatimid dynasty in Egypt created some of the most iconic Islamic structures, such as the Al-Azhar Mosque and the Al-Hakim Mosque. Meanwhile, in Central Asia, the Seljuk Turks were building stunning Islamic architecture examples, including the Kharaghan twin towers and the Sultan Ahmed Mosque in Istanbul. The expansion of Islamic architecture continued into the 14th and 15th centuries, with the construction of magnificent buildings like the Timurid-era Gur-e Amir mausoleum in Uzbekistan and the Ottoman-era Topkapi Palace in Istanbul.
Islamic architecture influences perhaps reached its zenith in the 16th and 17th, with a flowering of artistic and cultural achievements under the patronage of powerful empires, particularly the Ottomans and the Mughals. Ottoman architecture was characterised by the use of intricate tile work, domes, and arches, as exemplified by the famed Blue Mosque in Istanbul. Mughal architecture, on the other hand, blended Indian and Persian elements with Islamic motifs, creating masterpieces such as the Taj Mahal in Agra. Both empires were influenced by the classical Islamic architectural traditions, particularly the use of geometric patterns, calligraphy, and ornate decoration. Islamic architecture in this period reflected the political and cultural aspirations of these empires, creating enduring legacies that continue to inspire architects and designers today.
Also read: Expert talks: Can Architects Specialise in Both BIM and Computational Design?

The global influence of Islamic architecture in the medieval era cannot be overstated. As the Islamic empire expanded across North Africa, the Middle East, and Central Asia, it brought with it a rich and diverse architectural tradition that drew on a range of influences from ancient Persia, Greece, Rome, and Byzantium.

Islamic architectural styles were characterised by the use of intricate geometric patterns, decorative calligraphy, and complex interlocking forms that emphasised the unity and harmony of the universe. These stylistic Islamic architecture elements spread to other regions through trade and cultural exchange, influencing the design of buildings in Europe, Africa, and Asia. The influence of Islamic architecture can be seen in structures like the Alhambra palace in Spain, the Taj Mahal in India, and the Great Mosque of Xi'an in China, which all incorporate Islamic architecture elements.
Islamic architecture is renowned for its stunning beauty, intricate details, and ornate designs. At the heart of this architectural tradition are several key design Islamic architecture elements that are commonly found in Islamic buildings across the world.
Also Read: 10 Respected Parametric Design Firms in India to Look Out For

Also Read: Interesting Trends in the Use of Rhino 3D in the Indian Design Industry
Features of Islamic Architecture
Islamic architecture is one of the most historically significant styles, showcasing prevalent characteristics across various countries. Noting these meticulous elements alongside urban context is the only way to understand their visual and stimulating features and style. So, let's dive into some Islamic architecture characteristics:
1. Geometric Patterns
One of the most distinctive features of Islamic architecture is its use of geometric patterns. These patterns, which are often based on complex mathematical formulas, are used to create intricate designs on everything from floors and walls to ceilings and domes. In Islamic architecture, geometric patterns are used to convey a sense of harmony and unity, reflecting the belief that everything in the universe is interconnected.
2. Calligraphy
Another key feature of Islamic architecture is the use of calligraphy. Islamic calligraphy, which is considered one of the highest forms of art in the Islamic world, is used to adorn everything from walls and doorways to textiles and ceramics. The Arabic language, which is used for Islamic calligraphy, is considered sacred, and its use in architectural design reflects the importance of language and communication in Islamic culture.
3. Arched Domes and Vaults
Islamic architecture is also known for its use of arched domes and vaults, which are used to create dramatic, soaring spaces that inspire awe and wonder. These architectural features are often decorated with intricate patterns and designs, adding to their visual impact.
4. Muqarnas
Islamic architects also developed several innovative techniques to allow them to create the intricate designs and patterns that are a hallmark of Islamic architecture. One such technique is the use of muqarnas, which are ornamental niches or corbels that create the illusion of a three-dimensional structure and are one of the most prominent features of Islamic architecture. Another technique is the use of stalactite vaults, which create a visually striking effect by tapering inward as they rise towards the ceiling.
5. Charbagh Gardens
Charbagh gardens are a key feature of Islamic architecture and are commonly found in Islamic gardens and palaces. These gardens are based on a four-fold division of space, with the garden being divided into four equal quadrants. The quadrants are often arranged around a central water feature, such as a pool or fountain, and are designed to represent the four rivers of paradise in Islamic tradition. Charbagh gardens are characterised by their use of symmetry, geometry, and lush greenery, and are a testament to the Islamic appreciation of beauty, harmony, and balance in the natural world.
Perhaps one of the best Islamic architecture examples embodying all of these elements is the Taj Mahal in Agra. It features a stunning combination of geometric patterns and calligraphy, with intricate designs carved into white marble. Arched domes and vaults add to the grandeur of the structure, while the muqarnas enhance the aesthetic appeal. The Charbagh gardens surrounding the Taj Mahal offer a perfect blend of symmetry and nature. Together, these features reinforce the position of the Taj Mahal as an enduring symbol of love and beauty.
Also Read: Top 6 Verticals of Computational Design Every Architect Must Know
The cultural significance of Islamic architecture is nothing short of remarkable. In an era defined by global trade and travel, its influence has transcended national boundaries, seeping into the very fabric of buildings, monuments, and art forms across continents. Its distinctive artistic style, rooted in a rich cultural heritage, has indelibly marked the world. Even in modern times, the enduring impact of Islamic architecture concepts on contemporary design is palpable. It is a testament to the enduring legacy of this remarkable art form that its influence remains as potent today as it did centuries ago.

Conclusion
Islamic architecture is known for its magnificent domes, intricate geometric patterns, and grand pointed arches that have eyes glued from the world for centuries. The admirers appreciate the art form and the imagination around meticulous detailing, symmetrical contours, and splendid hues, with lures of Islamic architecture knowing no boundaries.
Also, did you know that you can also create intricate and complex designs by upskilling and taking our Masters in Computational Design Course. This course will help you understand computation in different design fields with industry workflows, advanced tools for a concrete foundation in computational design. Learn high-performance computational building information modelling (BIM) and building analysis via a live industry project. Get an opportunity to pursue professional certification, along with endless career possibilities and upskilling.
Subscribe to Novatr
Always stay up to date with what’s new in AEC!
Get articles like these delivered to your inbox every two weeks.

 Thanks for connecting!
Thanks for connecting!

.png)
-1.png)