Plants 2023, 12(4), 749; https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12040749 - 7 Feb 2023
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1860
Abstract
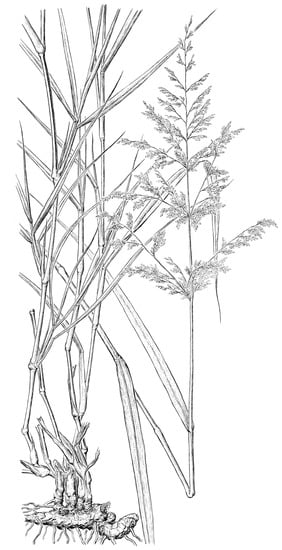
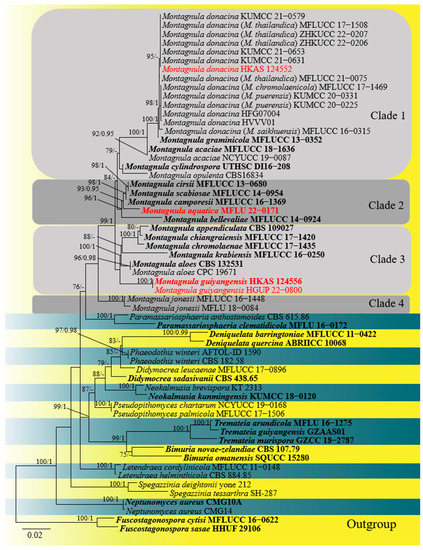
Subtribe Cenchrinae, so-called as the “bristle clade”, is a monophyletic group of panicoid grasses characterized by having sterile branches or bristles on the inflorescences in most of its species. Within this subtribe is also placed Panicum antidotale Retz., an “incertae sedis” species of
[...] Read more.
Subtribe Cenchrinae, so-called as the “bristle clade”, is a monophyletic group of panicoid grasses characterized by having sterile branches or bristles on the inflorescences in most of its species. Within this subtribe is also placed Panicum antidotale Retz., an “incertae sedis” species of Panicum L. which lacks bristles along the inflorescence. In this study, we present an update of the subtribe Cenchrinae based on molecular, morphological, and anatomical evidence to clarify the systematic position of P. antidotale in the Cenchrinae, excluding it from Panicum and establishing it in a new genus (i.e., Janochloa Zuloaga & Delfini); the morphological features distinguishing the new genus from other closely related taxa are properly discussed and an identification key to the 24 genera recognized within Cenchrinae is presented. We also add American Setaria species, not tested before, of subgenera Paurochaetium and Reverchoniae, discussing the position of these taxa in actual phylogeny of the genus as well as defining placements in the tree of Setaria species that were imprecisely located in previous analyses. A comparison with the results from other studies, comments on Stenotaphrum Trin. and a brief discussion on conflicting placements in Cenchrus and related taxa, and of Acritochaete Pilg. are also included.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Plant Systematics and Taxonomy)
►
Show Figures