Abstract
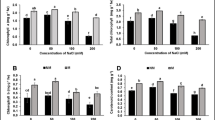
Long-term excessive use of chemical fertilizers led to serious environmental pollution and food safety problems. Natural biostimulants are complimentary to pesticides and fertilizers, which can regulate plant growth and metabolism via promoting nutrient absorption and improving the ability to resist abiotic stresses. Vegetal extract, rich in bioactive substances, is one type of biostimulants. We determined the concentration of predominant active compound aloe-emodin in Rheum officinale Baill (R. officinale) extracts using LC–MS/MS. We applied either R. officinale extracts or aloe-emodin to tomato seedlings at the vegetative stage via different ways including spraying foliar (S), root irrigation (R) or spraying foliar and root irrigation (SR). Both R. officinale crude extracts and aloe-emodin could promote the growth of tomato stem and root, improve the photosynthetic capacity of leaves, improve the biomass of tomato, and ultimately lead to the vigorous growth of tomato plants. Clustering analysis and correlation analysis further confirmed that the effect was best in R application mode. Extracts of R. officinale and its active component aloe-emodin have been shown to increase the growth of tomato seedlings, implying that R. officinale could be a source of biostimulants.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre E, Lemenager D, Bacaicoa E, Fuentes M, Baigorri R, Zamarreno AM, Garcia-Mina JM (2009) The root application of a purified leonardite humic acid modifies the transcriptional regulation of the main physiological root responses to Fe deficiency in Fe-sufficient cucumber plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 47:215–223
Akbudak MA, Filiz E, Çetin D (2022) Genome-wide identification and characterization of high-affinity nitrate transporter 2 (NRT2) gene family in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) and their transcriptional responses to drought and salinity stresses. J Plant Physiol 272:153684
Alehaideb Z, Chin KC, Yao MC, Law FCP (2019) Predicting the content of anthraquinone bioactive in Rhei rhizome (Rheum officinale Baill.) with the concentration addition model. Saudi Pharm J 27:25–32
Barow M, Meister A (2003) Endopolyploidy in seed plants is differently correlated to systematics, organ, life strategy and genome size. Plant Cell Environ 26:571–584
Bi D, Yang X, Lu J, Xu X (2022) Preparation and potential applications of alginate oligosaccharides. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2022.2067832
Brown P, Saa S (2015) Biostimulants in agriculture. Front Plant Sci 6:671
Cameron A, Sarojini V (2014) Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae: chemical control, resistance mechanisms and possible alternatives. Plant Pathol 63:1–11
Castiglione AM, Mannino G, Contartese V, Bertea CM, Ertani A (2021) Microbial biostimulants as response to modern agriculture needs: composition, role and application of these innovative products. Plants-Basel 10:1533
Chan ZL (2012) Expression profiling of ABA pathway transcripts indicates crosstalk between abiotic and biotic stress responses in Arabidopsis. Genomics 100:110–115
Chen L, Li J, Zhu Y, Guo L, Ji R, Miao Y, Guo L, Du H, Liu D (2021) Caffeic acid, an allelochemical in Artemisia argyi, inhibits weed growth via suppression of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway and the biosynthesis of gibberellin and phytoalexin. Front Plant Sci 12:802198
Chen L, Li JX, Zhu YY, Zhao TT, Guo LJ, Kang LP, Yu JQ, Du HZ, Liu DH (2022) Weed suppression and molecular mechanisms of isochlorogenic acid a isolated from Artemisia argyi extract via an activity-guided method. J Agric Food Chem 70:1494–1506
Chennappa G, Sreenivasa MY, Nagaraja H (2018) Azotobacter salinestris: a novel pesticide-degrading and prominent biocontrol PGPR bacteria. In: Microorganisms for green revolution, Vol 2: microbes for sustainable agro-ecosystem, vol 7, p 23–43
Dong X, Fu J, Yin X, Cao S, Li X, Lin L, Ni J (2016) Emodin: a review of its pharmacology, toxicity and pharmacokinetics. Phytother Res 30:1207–1218
du Jardin P (2015) Plant biostimulants: definition, concept, main categories and regulation. Sci Hortic 196:3–14
Ebinezer LB, Franchin C, Trentin AR, Carletti P, Trevisan S, Agrawal GK, Rakwal R, Quaggiotti S, Arrigoni G, Masi A (2020) Quantitative proteomics of maize roots treated with a protein hydrolysate: a comparative study with transcriptomics highlights the molecular mechanisms responsive to biostimulants. J Agric Food Chem 68:7541–7553
Ertani A, Pizzeghello D, Baglieri A, Cadili V, Tambone F, Gennari M, Nardi S (2013) Humic-like substances from agro-industrial residues affect growth and nitrogen assimilation in maize (Zea mays L.) plantlets. J Geochem Explor 129:103–111
Gao HY, Li NN, Li JH, Khan A, Ahmad I, Wang YY, Wang FY, Luo HH (2021) Improving boll capsule wall, subtending leaves anatomy and photosynthetic capacity can increase seed cotton yield under limited drip irrigation systems. Ind Crops Prod 161:113214
Jing JY, Zhang SQ, Yuan L, Li YT, Zhang YQ, Zhao BQ (2022) Synergistic effects of humic acid and phosphate fertilizer facilitate root proliferation and phosphorus uptake in low-fertility soil. Plant Soil. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-022-05486-2
Kou SG, Peters LM, Mucalo MR (2021) Chitosan: a review of sources and preparation methods. Int J Biol Macromol 169:85–94
Kulkarni MG, Stirk WA, Southway C, Papenfus HB, Swart PA, Lux A, Vaculik M, Martinka M, Van Staden J (2013) Plant growth regulators enhance gold uptake in Brassica juncea. Int J Phytoremediation 15:117–126
Li JX, Chen L, Chen QH, Miao YH, Peng Z, Huang BS, Guo LP, Liu DH, Du HZ (2021) Allelopathic effect of Artemisia argyi on the germination and growth of various weeds. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-83752-6
Liu M, Yang Q, Hua Q, Liu J, He W, Niu D, Liu X (2021) Chinese medicinal herbs for idiopathic membranous nephropathy in adults with nephrotic syndrome: a systematic review of effectiveness and safety. Medicine (baltimore) 100:e27953
Liu Y, Roof S, Ye Z, Barry C, van Tuinen A, Vrebalov J, Bowler C, Giovannoni J (2004) Manipulation of light signal transduction as a means of modifying fruit nutritional quality in tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:9897–9902
Ma ZX, Garrido-Maestu A, Jeong KC (2017) Application, mode of action, and in vivo activity of chitosan and its micro and nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: a review. Carbohydr Polym 176:257–265
Niu CX, Wang G, Sui J, Liu GZ, Ma FF, Bao ZL (2022) Biostimulants alleviate temperature stress in tomato seedlings. Sci Hortic 293:110712
Panfili I, Bartucca ML, Marrollo G, Povero G, Del Buono D (2019) Correction to application of a plant biostimulant to improve maize (Zea mays) tolerance to metolachlor. J Agric Food Chem 67:14005
Potok ME, Zhong Z, Picard CL, Liu Q, Do T, Jacobsen CE, Sakr O, Naranbaatar B, Thilakaratne R, Khnkoyan Z, Purl M, Cheng H, Vervaet H, Feng S, Rayatpisheh S, Wohlschlegel JA, O’Malley RC, Ecker JR, Jacobsen SE (2022) The role of ATXR6 expression in modulating genome stability and transposable element repression in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2115570119
Qian G, Xu L, Li N, Wang K, Qu Y, Xu Y (2022) Enhanced arsenic migration in tailings soil with the addition of humic acid, fulvic acid and thiol-modified humic acid. Chemosphere 286:131784
Rahimi A, Mohammadi MM, Moghaddam SS, Heydarzadeh S, Gitari H (2022) Effects of stress modifier biostimulants on vegetative growth, nutrients, and antioxidants contents of garden thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.) under water deficit conditions. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-022-10604-6
Salas-Gonzalez I, Reyt G, Flis P, Custodio V, Gopaulchan D, Bakhoum N, Dew TP, Suresh K, Franke RB, Dangl JL, Salt DE, Castrillo G (2021) Coordination between microbiota and root endodermis supports plant mineral nutrient homeostasis. Science 371:143
Santamaria-Hernando S, Lopez-Maroto A, Galvez-Roldan C, Munar-Palmer M, Monteagudo-Cascales E, Rodriguez-Herva JJ, Krell T, Lopez-Solanilla E (2022) Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato infection of tomato plants is mediated by GABA and l-Pro chemoperception. Mol Plant Pathol 23:1433–1445
Song SY, Liu GZ, Ma FF, Bao ZL (2022) Brassinazole represses tomato hypocotyl elongation via inhibition of cell division. Plant Growth Regul 96:463–472
Sukkasam N, Incharoensakdi A, Monshupanee T (2022) Disruption of hydrogen gas synthesis enhances the cellular levels of NAD(P)H, glycogen, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and photosynthetic pigments under specific nutrient condition(s) in cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Plant Cell Physiol 63:135–147
Tian K, Zhang H, Chen X, Hu Z (2006) Determination of five anthraquinones in medicinal plants by capillary zone electrophoresis with beta-cyclodextrin addition. J Chromatogr A 1123:134–137
Torabian S, Farhangi-Abriz S, Rathjen J (2018) Biochar and lignite affect H(+)-ATPase and H(+)-PPase activities in root tonoplast and nutrient contents of mung bean under salt stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 129:141–149
Torres-Rodriguez JA, Reyes-Perez JJ, Castellanos T, Angulo C, Quinones-Aguilar EE, Hernandez-Montiel LG (2022) Identification and morphological characterization of marine actinomycetes as biocontrol agents of Fusarium solani in tomato. Revista De La Facultad De Agronomia De La Universidad Del Zulia 39:1
Wang JQ, Qin LJ, Cheng JR, Shang CC, Li B, Dang YC, He HS (2022) Suitable chemical fertilizer reduction mitigates the water footprint of maize production: evidence from Northeast China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:22589–22601
Wang MY, Chen YC, Zhang R, Wang WX, Zhao XM, Du YG, Yin H (2015) Effects of chitosan oligosaccharides on the yield components and production quality of different wheat cultivars (Triticum aestivum L.) in Northwest China. Field Crop Res 172:11–20
Wu JB, Zhao H, Wang XD (2022) Soil microbes influence nitrogen limitation on plant biomass in alpine steppe in North Tibet. Plant Soil 474:395–409
Xiao TT, Boada R, Marini C, Llugany M, Valiente M (2020) Influence of a plant biostimulant on the uptake, distribution and speciation of Se in Se-enriched wheat (Triticum aestivum L. cv. Pinzon). Plant Soil 455:409–423
Xu Y, Wieloch T, Kaste JAM, Shachar-Hill Y, Sharkey TD (2022) Reimport of carbon from cytosolic and vacuolar sugar pools into the Calvin–Benson cycle explains photosynthesis labeling anomalies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 119:e2121531119
Yan X, Gu S, Shi Y, Cui X, Wen S, Ge J (2017) The effect of emodin on Staphylococcus aureus strains in planktonic form and biofilm formation in vitro. Arch Microbiol 199:1267–1275
Yang X, Ma X, Yang L, Yu D, Qian Y, Ni H (2009) Efficacy of Rheum officinale liquid formulation on cucumber powdery mildew. Crop Prot 28:1031–1035
Yazaki K, Matsuoka H, Shimomura K, Bechthold A, Sato F (2001) A novel dark-inducible protein, LeDI-2, and its involvement in root-specific secondary metabolism in Lithospermum erythrorhizon. Plant Physiol 125:1831–1841
Zhang J, Chi F, Wei D, Zhou B, Cai S, Li Y, Kuang E, Sun L, Li LJ (2019) Impacts of long-term fertilization on the molecular structure of humic acid and organic carbon content in soil aggregates in black soil. Sci Rep 9:11908
Zhang YR, Liu YR, Tang ZS, Song ZX, Zhang JW, Chang BJ, Zhao ML, Xu J (2022) Rheum officinale Baill. Treats zebrafish embryo thrombosis by regulating NOS3 expression in the arginine biosynthesis pathway. Phytomedicine 99:153967
Zheng TC, Zhuo XK, Li LL, Wang J, Cheng TR, Zhang QX (2019) Genome-wide analysis of the d-type cyclin gene family reveals differential expression patterns and stem development in the woody plant Prunus mume. Forests 10:147
Zhu HY, Wang XT, Wang XM, Pan GX, Zhu Y, Feng YX (2021) The toxicity and safety of Chinese medicine from the bench to the bedside. J Herb Med 28:100450
Acknowledgements
We thank plant growth facility members in the state key laboratory of crop biology at Shandong Agricultural University.
Funding
This work was supported by Key research and development program of Shandong Province (2021LZGC017), Taishan Scholar Foundation of Shandong Province (tsqn201812034), Agricultural Seed Project of Shandong Province (2020LZGC005) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (31872951).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZB, GL and FM conceived and designed the experiments. CX, MM, GL and JX performed most of experiments. GL, JX and CX analyzed the data. JL provided technical support. DF provided materials and resources. GL, FM and ZB wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Conflict of interest the authors declare no potential conflict of interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Pramod Kumar Nagar.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, C., Ma, M., Xin, J. et al. The active compound in Rheum officinale Baill, aloe-emodin promotes tomato seedling growth. Plant Growth Regul 102, 213–226 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-023-00995-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-023-00995-1