Valerian Plant
- December 27, 2023
- 0 comment
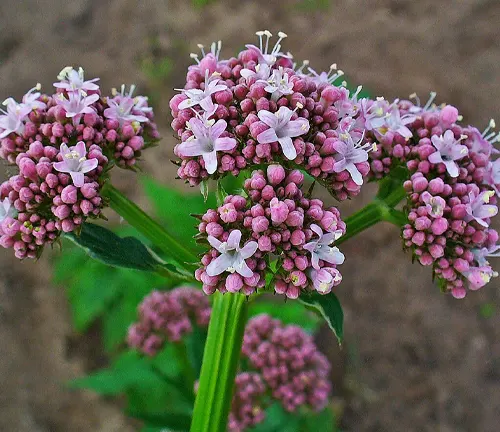
The Valerian plant, scientifically known as Valeriana officinalis, is a perennial herb that has been revered for its medicinal properties for centuries. Native to Europe and parts of Asia, this herb is characterized by its delicate clusters of sweetly scented pink or white flowers that bloom in the summer. The plant’s root, however, is the primary source of its therapeutic benefits. Valerian has long been employed as a natural remedy to alleviate conditions such as insomnia and anxiety.
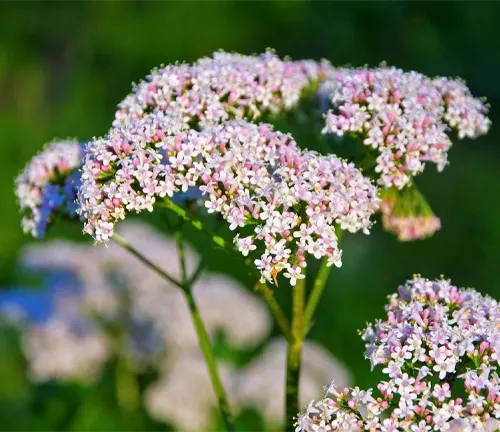

Its root contains compounds that interact with the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors in the brain, promoting a calming effect and aiding in relaxation. Due to its sedative properties, Valerian is often used to improve sleep quality and treat mild nervous tension. Additionally, it has been historically utilized to address various ailments, including headaches and digestive issues. Valerian is commonly available in the form of supplements, teas, or tinctures, making it a popular choice for those seeking a natural approach to managing stress and sleep disorders.
However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating Valerian into one’s wellness routine, as individual responses to herbal remedies can vary.
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Valeriana officinalis |
| Common Names | Valerian, Garden Valerian, All-Heal |
| Family | Caprifoliaceae |
| Type | Perennial herb |
| Native Regions | Europe, Asia |
| Height | Typically 1 to 2 meters (3 to 6 feet) |
| Flowers | Clusters of sweetly scented pink or white |
| Part Used | Root |
| Medicinal Properties | Sedative, anxiolytic, nervine |
| Active Compounds | Valerenic acid, Valeranon, Valepotriates |
| Traditional Uses | Sleep aid, anxiety relief, stress management |
| Mode of Consumption | Supplements, teas, tinctures |
| Interactions | Consultation with healthcare professional |
| Caution | Potential for drowsiness; avoid heavy machinery |
| Availability | Widely available as herbal supplements |
| Other Uses | Historical remedy for headaches, digestive issues |
| Research Status | Ongoing studies on effectiveness for sleep disorders |
Unveiling the Allure of the Valerian Plant
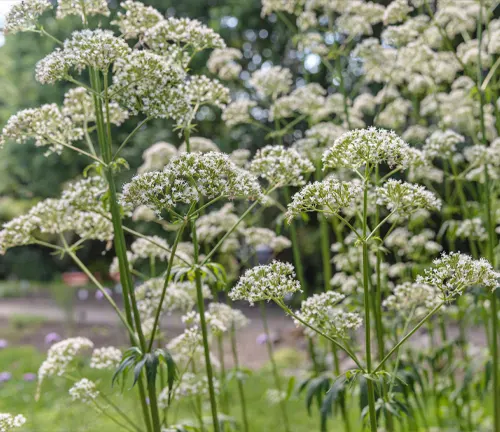

In the enchanting world of botanical wonders, the Valerian plant, scientifically known as Valeriana officinalis, stands as a testament to both beauty and utility. This perennial herb, native to Europe and Asia, graces woodlands with its delicate clusters of sweetly scented pink or white flowers. Delving into the intricate details of its botanical makeup reveals a plant that not only captivates the eye but also harbors medicinal treasures in its roots.
A Closer Look at Valerian’s Graceful Presence
A stroll through woodlands adorned with Valerian plants offers a glimpse into nature’s delicate artistry. The plant’s slender stems rise gracefully, showcasing clusters of fragrant blooms that add a touch of elegance to their surroundings. Understanding the botanical intricacies of Valerian enhances our appreciation for its aesthetic contributions to the natural landscape.
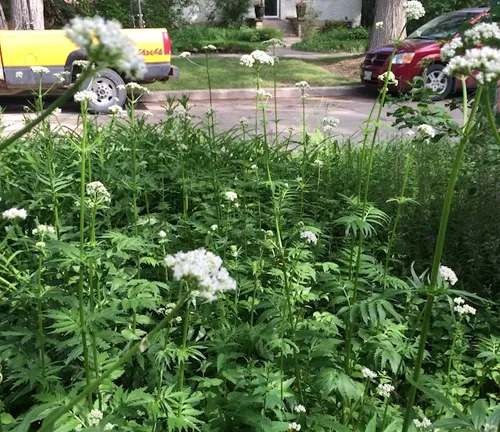
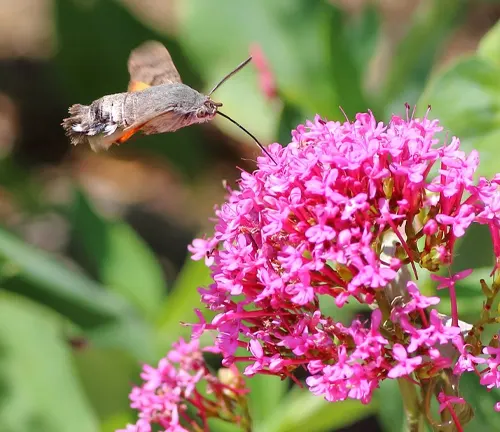


Ecological Importance: Valerian’s Role in the Ecosystem
Beyond its visual appeal, the Valerian plant plays a crucial role in the ecosystem. As a perennial herb, it provides habitat and sustenance for various insects and pollinators. Bees, butterflies, and other beneficial insects are drawn to its nectar-rich flowers, contributing to the intricate dance of biodiversity in the woodlands it calls home.
Nurturing Valerian for Future Generations
Valerian’s popularity extends beyond its native habitats, prompting cultivation efforts to meet the demand for its medicinal properties. However, this increased interest raises concerns about conservation. Balancing cultivation with responsible harvesting and conservation practices ensures the Valerian plant thrives for future generations, preserving both its ecological significance and medicinal potential.
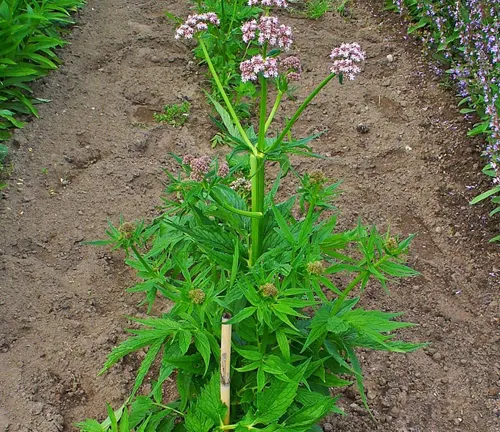

Valerian’s Underground Contribution
Beneath the surface, Valerian’s roots play a crucial role in soil stabilization. Their extensive network helps prevent soil erosion, making the plant a natural ally in maintaining the structural integrity of woodland ecosystems. This below-ground contribution adds to the plant’s ecological value, emphasizing its role as a guardian of environmental health.
Beyond the Woodland Veil
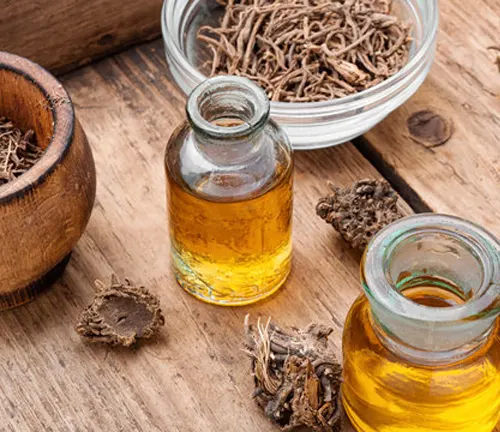

While Valerian’s woodland elegance and ecological importance are well-established, its uses extend beyond the confines of the forest. Humans have recognized its potential for centuries, employing the plant for various purposes. From traditional herbal remedies to modern supplements, Valerian has woven itself into the fabric of herbal medicine, addressing ailments and promoting well-being.
Unveiling the Medicinal Magic of Valerian
Valerian’s roots harbor medicinal compounds that have earned it a place in the realm of natural remedies. Its sedative and anxiolytic properties make it a sought-after solution for managing insomnia and stress. As research continues to explore its potential benefits, Valerian stands as a botanical beacon, offering a natural alternative for those seeking calm and tranquility in a bustling world.

Tracing the Valerian Plant’s Natural Abode
Embarking on a journey to understand the Valerian plant involves mapping its habitat, revealing the regions where this captivating perennial herb thrives. With roots in Europe and parts of Asia, the Valerian plant graces woodlands, meadows, and the fringes of streams. Exploring its habitat map unveils the geographical tapestry that Valeriana officinalis paints, offering insights into the natural conditions that foster its growth.
Delving into Valerian’s Medicinal Chemistry
Unlocking the mysteries of the Valerian plant involves a closer look at its components, particularly the potent compounds nestled in its roots. Valerian boasts a rich chemical profile, with valerenic acid, valeranon, and valepotriates taking center stage. These compounds interact with the brain’s receptors, imparting the plant’s renowned sedative and anxiolytic properties. Understanding the chemistry behind Valerian’s efficacy unveils the herbal alchemy that has made it a time-honored remedy.
Navigating the Nuances of Valerian’s Impact
While the Valerian plant has earned acclaim for its therapeutic benefits, it’s crucial to navigate the side effect saga associated with its use. Commonly reported side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, and gastrointestinal disturbances. Unraveling the nuances of Valerian’s impact on different individuals sheds light on the importance of cautious consumption. Acknowledging potential side effects helps users make informed decisions, ensuring a balanced approach to harnessing the plant’s medicinal properties.
Different Species
Valeriana officinalis
Commonly known as garden valerian, this is the most widely recognized species with pink or white fragrant flowers. It is the primary source of the herbal remedy used for its sedative properties.
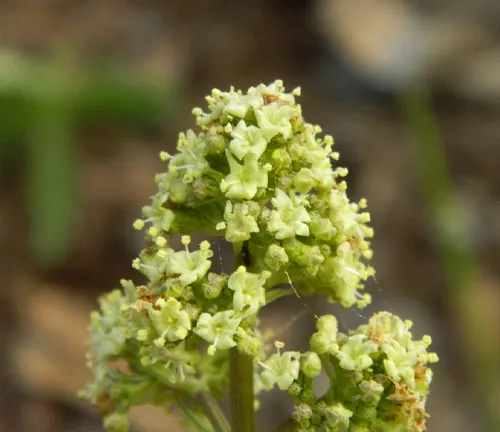


Valeriana edulis
Native to North America, Valeriana edulis, or the tobacco root, is a species with tuberous roots traditionally used by Native American tribes for medicinal purposes.
Valeriana sitchensis
Also known as Sitka valerian, this species is found in North America, particularly in the Pacific Northwest. It has clusters of white or pink flowers and is valued for its ornamental appeal.
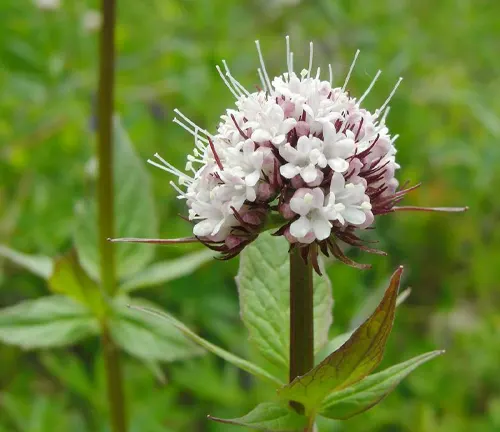
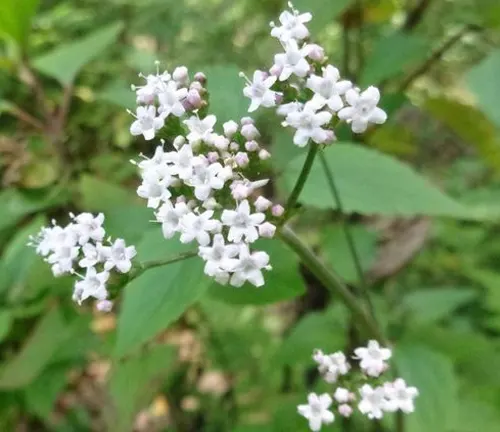


Valeriana jatamansi
Found in the Himalayan region, Valeriana jatamansi is used in traditional Ayurvedic medicine. It is known for its calming and anti-inflammatory properties.
Valeriana dioica
This dioecious species, commonly known as marsh valerian or water valerian, is found in wetlands and has distinctive male and female plants. It has pink or lavender flowers.
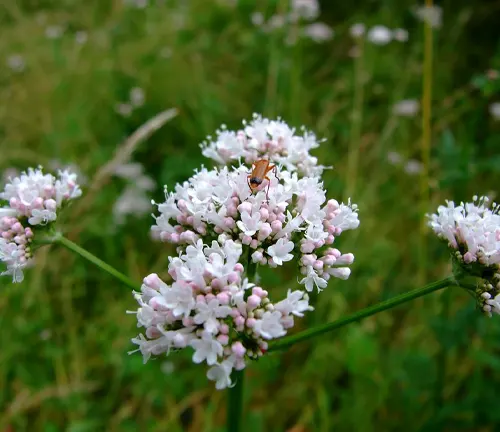
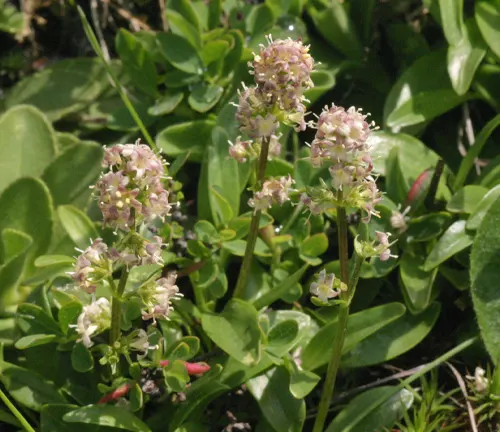


Valeriana celtica
Native to the Alps and other mountainous regions, Valeriana celtica, or alpine valerian, is a species with compact clusters of fragrant flowers. It is sometimes used in herbal medicine.
Valeriana pyrenaica
Endemic to the Pyrenees mountain range, this species, also known as Pyrenean valerian, features dense flower heads and is adapted to alpine environments.
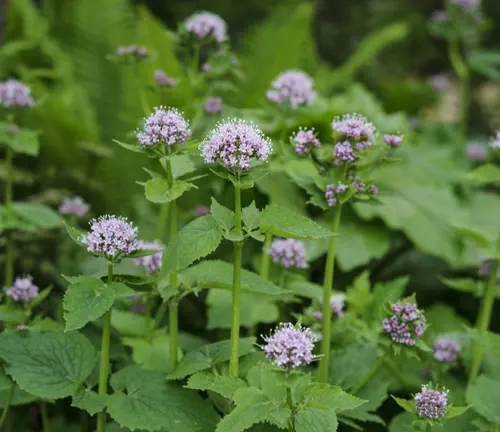
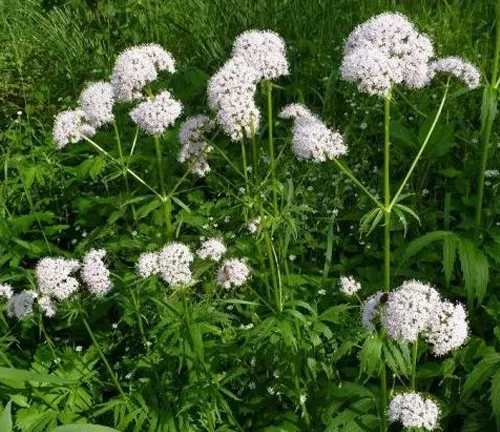


Valeriana wallichii
Native to the Himalayas, Valeriana wallichii is another species used in traditional Ayurvedic medicine. It is known for its potential sedative and tranquilizing effects.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is Valerian?
Valerian is a perennial herb, scientifically known as Valeriana officinalis, prized for its medicinal properties. It is native to Europe and Asia and is characterized by clusters of fragrant flowers. - What are the Medicinal Properties of Valerian?
Valerian is renowned for its sedative and anxiolytic properties. It interacts with GABA receptors in the brain, promoting relaxation and aiding in the management of conditions like insomnia and anxiety. - How is Valerian Used?
Valerian is commonly used in the form of supplements, teas, and tinctures. The root is the primary part used for its medicinal benefits. - Is Valerian Effective for Sleep Disorders?
Many people use Valerian to improve sleep quality and manage insomnia. Research suggests that it may help with sleep-related issues, but individual responses can vary. - Are There Any Side Effects of Valerian?
Common side effects may include drowsiness, dizziness, and gastrointestinal discomfort. It’s essential to use Valerian cautiously and consult with a healthcare professional, especially if taking other medications. - Can Valerian be Used for Anxiety?
Yes, Valerian is often used to alleviate mild anxiety. Its calming effects may help individuals manage stress and promote a sense of tranquility. - How Long Does it Take for Valerian to Work?
The onset of Valerian’s effects can vary among individuals. Some may experience benefits relatively quickly, while for others, it might take a few weeks of consistent use. - Can Valerian be Used by Pregnant or Nursing Women?
Pregnant and nursing women are advised to consult with a healthcare professional before using Valerian, as its safety during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not well-established. - Does Valerian Interact with Medications?
Valerian may interact with certain medications, including sedatives and anti-anxiety drugs. It’s crucial to inform healthcare providers about any herbal supplements being taken. - Can Valerian be Grown at Home?
Yes, Valerian can be grown in home gardens. It requires well-drained soil and partial shade. The root is typically harvested for medicinal use. - Is Valerian Safe for Long-Term Use?
While short-term use is generally considered safe, the safety of long-term use is not well-established. It’s advisable to use Valerian intermittently and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.














Leave your comment