The use of captured German 88-mm anti-aircraft guns

German 88-mm cannons, also known as "Acht-Komma-Аcht Zentimeter" (eight, eight centimeters) have become the same symbol of the German weapons World War II, as a Ju 87 bomber or a Pz.Kpfw.VI Tiger Ausf.E.
Anti-aircraft 88-mm guns were used not only against aviation, with a shortage of specialized anti-tank guns, they were successfully used to combat well-protected medium and heavy tanksas well as in coastal defense.
After the defeat of Germany in the First World War, it was forbidden to have and create anti-aircraft artillery, and already built anti-aircraft guns were subject to destruction. In this regard, work on the design and implementation of new anti-aircraft guns in metal was carried out in Germany secretly or through shell companies in other countries. For the same reason, all anti-aircraft guns, designed in Germany before 1933, had the designation "arr. 18". Thus, in case of inquiries from representatives of England and France, the Germans could answer that these were not new weapons, but old ones, created during the First World War.
In the second half of the 1920s, when designing in Germany anti-aircraft guns designed to counter high-altitude (by the standards of those years) air targets, the 75-mm caliber was initially considered. Work on such artillery systems was carried out by Rheinmetall-Borsig AG and Friedrich Krupp AG.
In the late 1920s, Rheinmetall-Borsig AG created several experimental 75 mm guns with barrel lengths of 55 and 59 calibers. However, these anti-aircraft guns were not adopted by the Reichswehr. As part of military cooperation, the gun, known as the 7,5 cm Flak L / 59, was offered to the USSR.
The original samples, made in Germany, were tested at the Research Anti-Aircraft Range in February-April 1932. In the same year, this gun, converted to a caliber 76,2 mm, was put into service in the USSR under the designation “76 mm anti-aircraft gun mod. 1931 " (3-K).
Anti-aircraft gun "arr. 1931 " was a completely modern weapon with good ballistic characteristics for that time. Its carriage with four folding beds provided circular fire, with a projectile weight of 6,5 kg, its height reach was 9 km. Rate of fire - 15 rds / min. The mass in the firing position is 3750 kg, in the stowed position - 4970 kg.
In 1930, the designers of Friedrich Krupp AG, working in Sweden, in agreement with Bofors, created the 7,5 cm Flak L / 60 anti-aircraft gun. In Sweden, the gun was mass-produced under the designation Bofors 75 mm Model 1929.

75-mm anti-aircraft gun 7,5 cm Flak L / 60
This 75-mm gun with a semi-automatic bolt and a cruciform platform was not officially accepted into service in Germany, but was actively produced for export. In 1939, the unrealized samples were requisitioned by the German Navy and used in the anti-aircraft units of the coastal defense. The Germans captured several dozen of these guns in Norway.
88 mm anti-aircraft guns 8,8 cm Flak 18/36/37/41
In 1928, the designers of Friedrich Krupp AG, who worked in Sweden, began to create an 88-mm anti-aircraft gun. When designing the new gun, the developments obtained during the creation of the 7,5 cm Flak L / 60 were used. Later, the design documentation was secretly delivered to Essen. And already in Germany, the first prototypes were made. The prototype was tested back in 1931, but the mass serial production of 88-mm guns began after Hitler came to power.
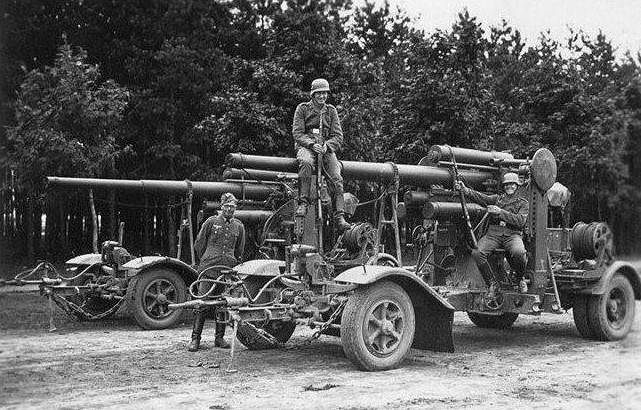

88 mm anti-aircraft guns 8,8 cm Flak 18 in transport position
For its time, it was a very perfect weapon, which is recognized as one of the best German artillery systems of the Second World War. The 88-mm anti-aircraft gun had very high characteristics for that time. A fragmentation projectile weighing 9 kg could hit targets at an altitude of up to 10600 m.
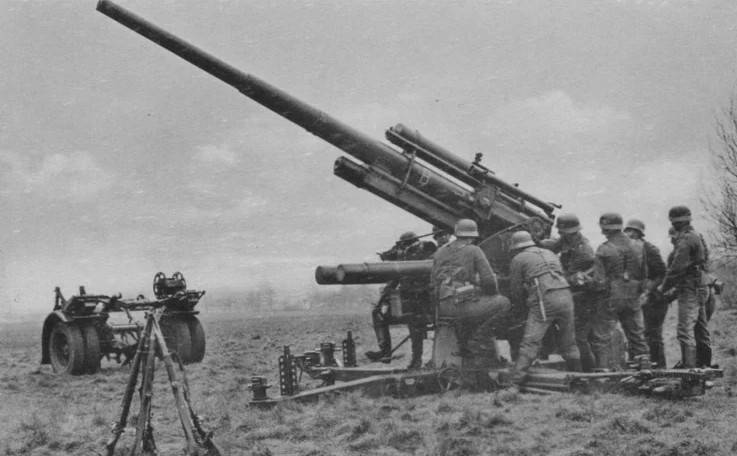

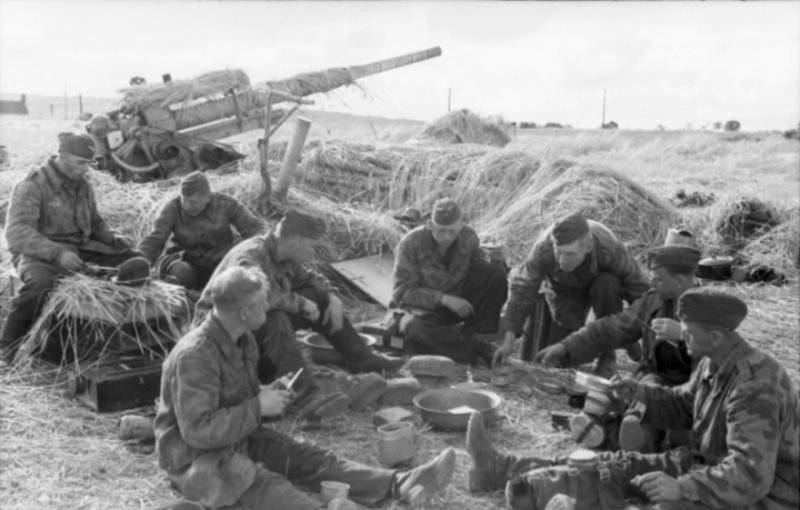
88-mm anti-aircraft gun in a firing position with the calculation
The maximum firing range at air targets was 14800 m. The mass of the gun in the firing position was 5000 kg. Rate of fire - up to 20 rds / min. Calculation - 10 people. Two single-axle trolleys were used for transportation. Towing was most often carried out by the Sd.Kfz. 7.

North Africa, German 88 mm anti-aircraft gun in tow of the Sd.Kfz. 7
The baptism of fire 8,8 cm Flak 18 took place in 1937 in Spain. Since there were few noteworthy air targets, the main purpose of the 88-mm anti-aircraft guns was shooting at ground targets. Five batteries of anti-aircraft artillery were concentrated in the vicinity of Burgos and Santander. During the Republican offensive at Terual, two batteries were used to defend Burgos, Almazana and Saragossa.
In March 1938, two batteries of German 88-mm guns supported the actions of the Francoists in the Villanev de Heva area with fire. At the same time, anti-aircraft guns were used with great success for counter-battery combat against Republican artillery. In the fall of 1938, the Flak 18s made a significant contribution to the defeat of the Republican forces during the Battle of the Ebro. 88-mm anti-aircraft guns, set to direct fire, destroyed firing points with high accuracy. At the end of hostilities, the Condor Legion had 52 Flak 18 guns.
The combat experience gained in Spain was subsequently taken into account when creating modernized models of 88-mm anti-aircraft guns. The most visible innovation was the shrapnel shield introduced on the part of the guns. In order to reduce the cost of production, the brass parts were replaced by those made of stainless steel.
For the 8,8 cm Flak 18, two different bogies were used (with single and dual wheels). And in order to unify on the modernized gun 8,8 cm Flak 36, they introduced a single gable bogie, which also made it easier to transport the anti-aircraft gun on soft soils. The introduction of a single transport trolley led to changes in the design of the gun. I had to unify the front and rear of the gun carriage. There was no other way to ensure the interchangeability of the carts.
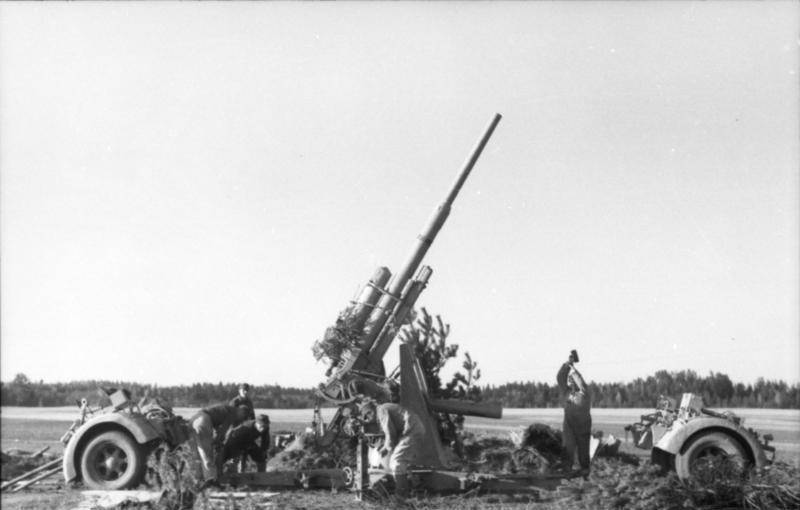

Transfer of the 8,8 cm Flak 36 to the firing position, the transport carts are already separated from the gun carriage
But the main modernization concerned the gun barrel, which received a detachable front part. At the same time, the ballistic characteristics of the gun and the rate of fire did not change.

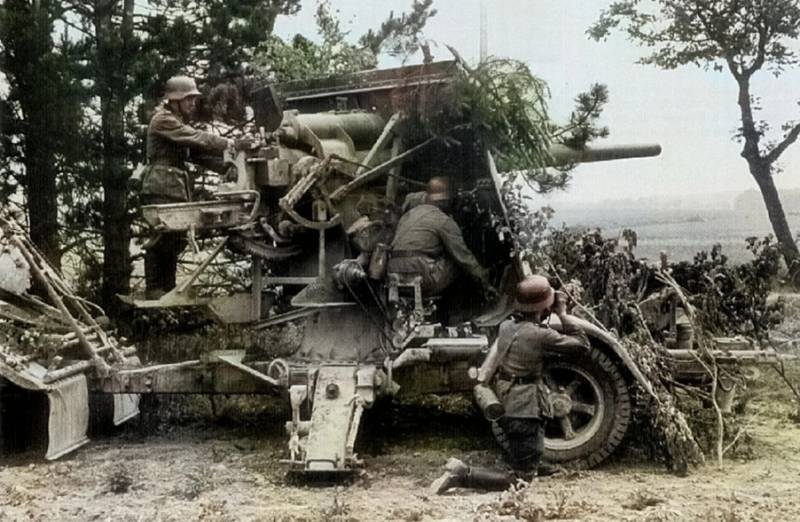
88-mm anti-aircraft gun 8,8 cm Flak 36 in a firing position with the calculation
In 1939, the production of the 8,8 cm Flak 37 anti-aircraft gun began. Outwardly, this model did not differ much from the 8,8 cm Flak 36. The modernization of the gun in this case did not affect the mechanical part, but the gun guidance system.
The Flak 37 guns were equipped with the Ubertransunger 37 automatic aiming system according to data transmitted by cable from the fire control equipment of the anti-aircraft battery. The 88-mm anti-aircraft guns of this modification were the first to be able to interface with the FuMG 62 Wurtzberg 39 fire control radar.
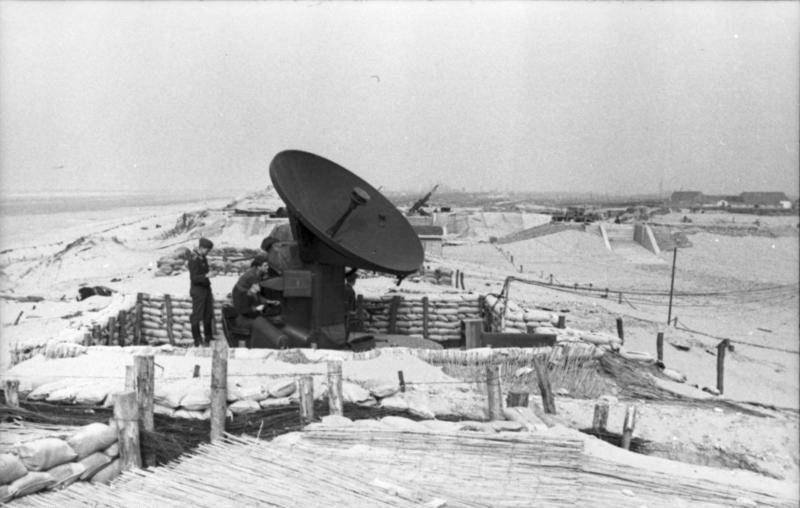

Anti-aircraft fire control radar FuMG 62 Wurtzberg 39
A radar with a parabolic antenna with a diameter of 3 meters, with a wavelength of 53 cm and a pulse power of up to 11 kW could correct anti-aircraft artillery fire at a distance of up to 29 km. At a distance of 10 km, the error in tracking an air target was 30–40 meters. The radar screen displayed not only air targets, but also the explosions of anti-aircraft shells.
Due to the fact that in the late 1930s the appearance of high-altitude reconnaissance aircraft and bombers operating at altitudes inaccessible to existing anti-aircraft guns was predicted, Rheinmetall-Borsig AG began work on an 88-mm gun with an increased range and height reach.
In 1941, a new anti-aircraft gun 8,8 cm Flak 41, adapted for firing ammunition with an enhanced propelling charge, entered the tests. A projectile weighing 9,4 kg left a two-section 72-caliber barrel (originally a three-section 74 caliber) with an initial speed of 1000 m / s. At the same time, the projectile could rise to a height of 14800 m. Thanks to the improved loading system, the rate of fire increased from 20 to 25 rds / min.
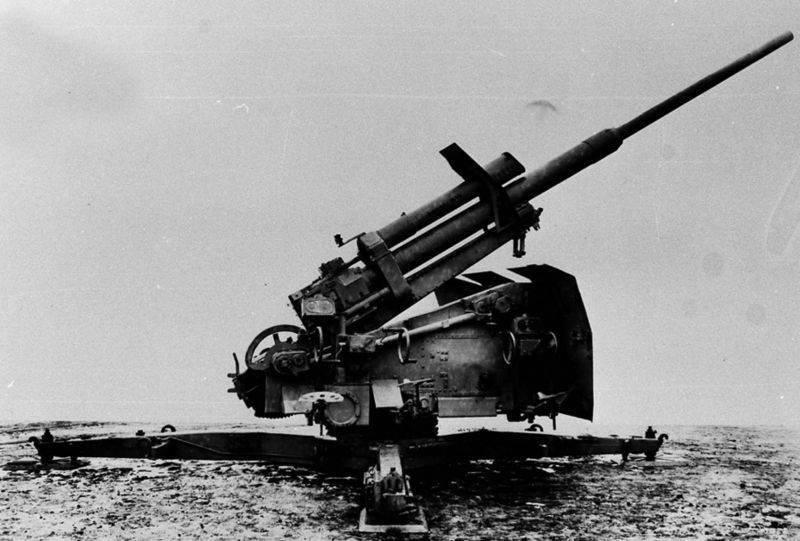
8,8 cm Flak 41 in firing position
To control the fire, the Kommandogerät 40 device was used, which was an optical rangefinder coupled with an analog mechanical computer.
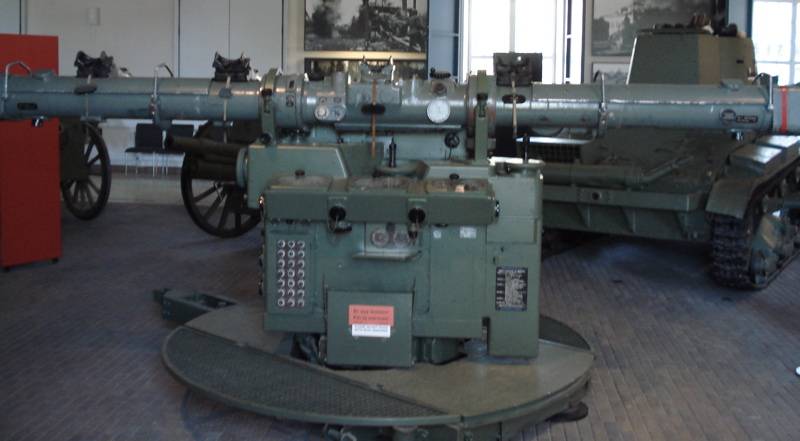

Kommandogerät 40 in the museum exposition
The Kommandogerät 40 device, serviced by a team of five people, made it possible to determine the flight parameters of an air target with high accuracy and transmit data to all four anti-aircraft battery guns in a semi-automatic mode via a wire line. This facilitated and significantly accelerated the process of targeting anti-aircraft guns, which ultimately increased the effectiveness of firing.
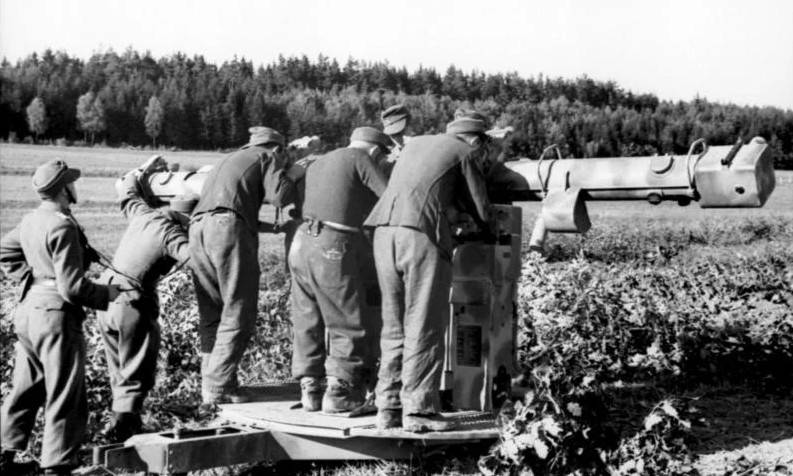

During the war years, the modified Kommandogerät 40 devices were also used to control the fire of other modifications of 88-mm anti-aircraft guns.
The 8,8 cm Flak 41 had the best performance in the family of German 88 mm anti-aircraft guns. But this weapon was quite expensive and difficult to manufacture. Before the surrender of Germany, only 556 units were produced. At the same time, 8,8 units were produced for 18 cm Flak 36/37/20754 guns.
In 1942, they tried to cross the Flak 41 barrel with the Flak 37 gun carriage. The tests of the "hybrid" were unsuccessful, the design could not withstand the increased load. Satisfactory results were achieved after strengthening a number of parts and introducing a muzzle brake.
Mass production was not possible due to overload with other orders. A total of 13 guns were fired, known as the 8,8 cm Flak 37/41. An attempt to produce a gun with a Flak 41 barrel on the carriage of a 105-mm anti-aircraft gun 10,5 cm FlaK 39 also failed.
In the initial period of World War II, 88-mm anti-aircraft guns played a leading role in ensuring the air defense of the territory of the Third Reich. As of September 1, 1939, the Luftwaffe anti-aircraft units had 2628 heavy anti-aircraft guns, the vast majority of which were 8,8 cm Flak 18/36/37. In Great Britain at that time there were about half as many anti-aircraft guns, which could be compared in range and reach with the German "acht-acht".
But even after 105 and 128-mm anti-aircraft guns were created and entered into service in Germany, 88-mm guns still made up the majority. In June 1944, the German armed forces had more than 10000 of these guns. 88-mm anti-aircraft guns were in service with anti-aircraft battalions of tank and infantry divisions, but even more often these guns were used in anti-aircraft units of the Luftwaffe.

88-mm anti-aircraft guns were also used as a versatile artillery in coastal defense. The guns installed on the coast were the first to open fire on enemy bombers flying from the sea. They also repeatedly had to engage in battle with fleet the enemy.
So, during Operation Agreement, conducted by the British on September 13-14, 1942 with the aim of disrupting the communications of the Axis countries in North Africa, in the vicinity of Tobruk, the fire of a battery of 88-mm anti-aircraft guns deployed on the coast was severely damaged and subsequently the destroyer HMS Sikh sank. (F82).
Of all the German anti-aircraft guns, the acht-acht played the most prominent role in anti-tank defense. Often, German heavy anti-aircraft guns were used to suppress enemy artillery batteries and provide fire support to ground forces.
In 1939, during the Polish campaign, heavy anti-aircraft batteries armed with Flak 18/36 guns were used very little for their intended purpose. MZA of 20-mm and 37-mm caliber perfectly coped with Polish aircraft flying at low altitudes, providing effective protection to their troops. During the entire campaign in Poland, heavy anti-aircraft batteries fired at Polish aircraft only a few times, but they were widely used to destroy ground targets.
In the course of hostilities in France, 88-mm anti-aircraft guns were very effective against French heavy Char B1 bis tanks and British infantry tanks Matilda Mk I.
The Flak 18/36 guns became a real "lifesaver" for the Germans, effective both in air defense and against ground targets. During the 1940 campaign in the West, the artillerymen of the 1st Anti-Aircraft Corps destroyed on the ground: 47 tanks and 30 bunkers. The 2nd Anti-Aircraft Corps, supporting the actions of the 4th and 6th armies, knocked out 284 tanks, destroyed 17 bunkers.
During the African campaign, the 88-mm anti-aircraft guns available in the German Afrika Korps proved to be a deadly anti-tank weapon, largely devaluing the British superiority in the number and quality of tanks.
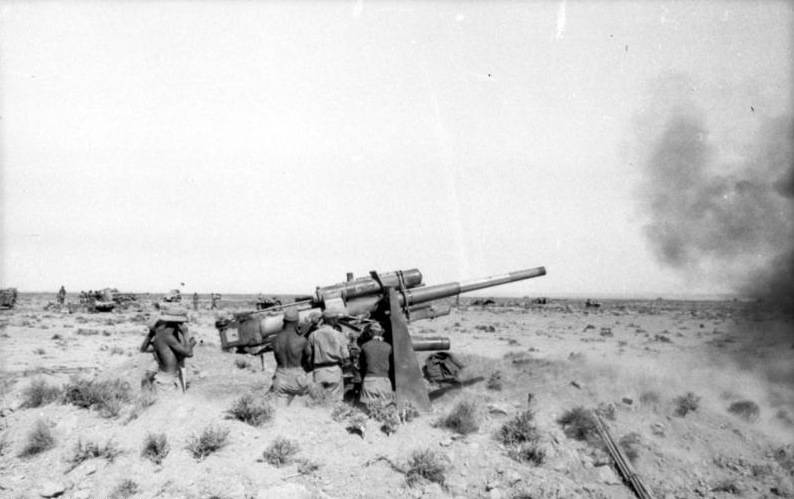

Rommel's troops, which arrived in Africa, initially had only 37-mm anti-tank guns 3,7 cm Pak 35/36, Pz.Kpfw tanks. II with a 20 mm cannon, Pz.Kpfw. III with a 37 mm cannon and a Pz.Kpfw. IV with a 75 mm short barreled cannon. The British had well-armored tanks Mk.VI Crusader, Matilda Mk.II, Valentine Mk.III, which were hardly vulnerable to German tank and anti-tank guns. Therefore, the 88-mm anti-aircraft guns were for the German troops the only effective means of dealing with enemy tanks.
If you do not take into account the corps artillery, in the summer of 1941, 88-mm anti-aircraft guns were the only German artillery systems capable of penetrating the frontal armor of heavy KV tanks.
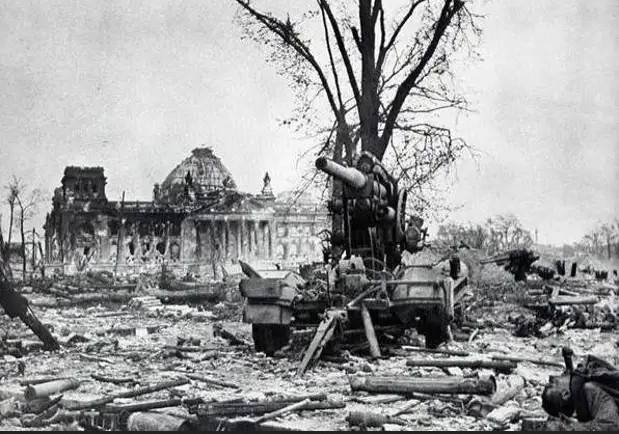

During the war, 88-mm towed anti-aircraft guns were actively used to combat Soviet, British and American tanks on all fronts. Especially their role in anti-tank defense increased after the transition of German troops to strategic defense. Until the second half of 1942, when the number of 88-mm guns on the leading edge was relatively small, not many T-34 and KV tanks were hit by them (3,4% - 88-mm guns). But already in the summer of 1944, 88-mm guns accounted for up to 38% of destroyed Soviet medium and heavy tanks, and with the arrival of our troops in Germany in the winter-spring of 1945, the percentage of destroyed tanks ranged from 50 to 70% (on different fronts). Moreover, the largest number of tanks was hit at a distance of 700-800 m.
These data are given for all 88-mm guns, but even in the 1945 year the number of 88-mm anti-aircraft guns significantly exceeded the number of 88-mm anti-tank guns of a special construction. Thus, at the last stage of the war, German anti-aircraft artillery played a significant role in land battles.
Use of 88 mm German anti-aircraft guns in the USSR
For the first time, several serviceable Flak 18 and Flak 36 were captured by our troops during the winter counteroffensive near Moscow.
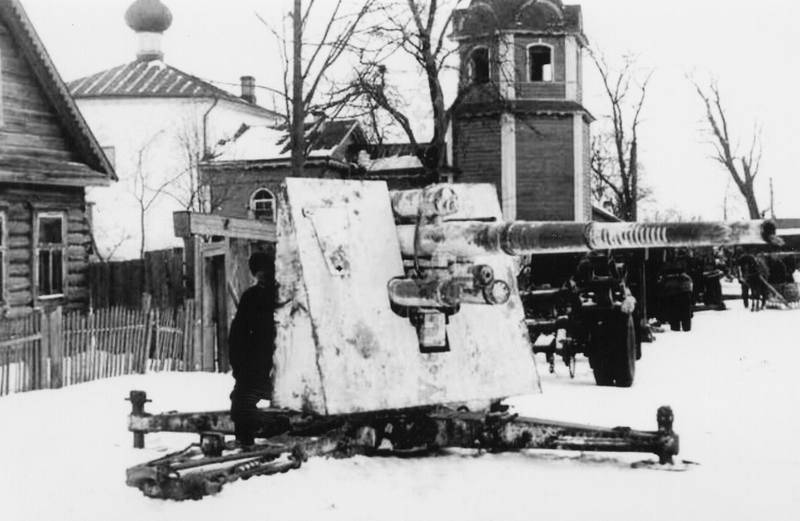

There is a possibility that the Red Army occasionally used a few 88-mm anti-aircraft guns against the former owners in 1942. But reliable information about the adoption of captured Flak 18 and Flak 36 dates back to 1943.
In a written report dated September 15, 1943, Marshal of Artillery N.N.Voronov mentioned that the artillery of the Voronezh Front had four artillery regiments armed with German-made anti-tank guns: 5 cm Pak. 38 and 7,5 cm Pak. 40. In addition, the report states that on 7 July, two large artillery regiments were handed over to the front, armed with 88 mm anti-aircraft guns, which were primarily intended for countering German armored vehicles and for counter-battery warfare.
Apparently, the captured 1943-mm anti-aircraft guns, which were commissioned in the summer of 88, were originally in service with the air defense units of the 6th Army, which was commanded by Field Marshal F. Paulus.
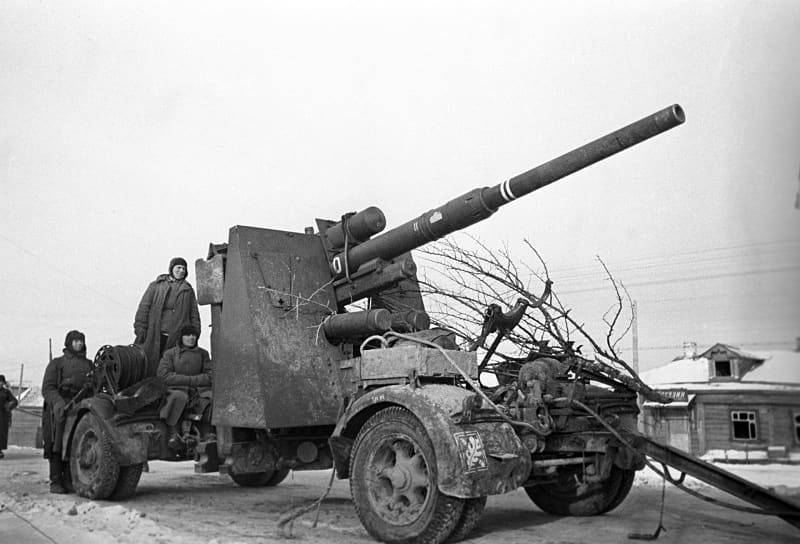

Now it is difficult to say why the heavy anti-aircraft guns captured by the Red Army were not used for their intended purpose. It can be assumed that the captured 88-mm anti-aircraft guns did not have serviceable fire control devices. In addition, the servicemen of the Red Army did not have firing tables and technical documentation translated into Russian. Our specialists managed to figure it out with shooting from captured anti-aircraft guns at ground targets, but conducting aimed fire at air targets was a much more complicated matter.
However, this situation persisted until the last days of the war. Several hundred captured 88 anti-aircraft guns were used exclusively as long-range guns for firing at targets deep in the German defenses.
Taking into account the fact that there was no particular sense in saving the resource of the captured German guns, and there was no shortage of ammunition, very often harassing fire was fired from them across the squares. In a number of cases, good results were obtained when shelling the front edge of the German defense. After a series of sighting shots, it was possible to achieve the operation of a remote fuse at a height of 5-10 m above the ground. With an air blast of a projectile, the effectiveness of the defeat of enemy manpower who took refuge in the trenches increased many times over.
In the post-war period, several hundred 88-mm anti-aircraft guns, which had a sufficient resource and good technical condition, were transferred to storage, where they were kept until the early 1960s. An unspecified number of German-made anti-aircraft guns with ammunition were handed over to the Allies, but most of them were cut into metal.
Use of German 88mm anti-aircraft guns in other countries
German 88mm anti-aircraft guns were popular with foreign buyers, and Germany exported several hundred guns.
China became the first importer of 8,8 cm Flak 18. In 1937, the Kuomintang government acquired 5 anti-aircraft batteries (20 guns). 88-mm cannons were actively used in repelling Japanese air raids in the battles of Chongqing and Chengdu. The guns deployed in the fortifications along the Yangtze fired at the advancing Japanese forces. At the same time, several Flak 18s were captured by the Japanese.
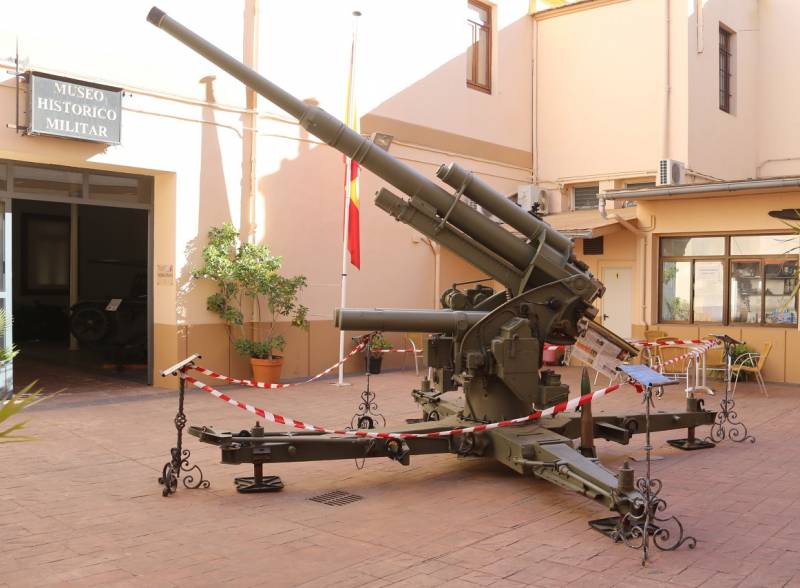
After the civil war, Spain bought 88 8,8 cm Flak 36 guns, and in 1943 their licensed production began at the Trubiya plant. Until 1947, more than 44 guns were produced under the designation FT 200. The service of the German 88-mm anti-aircraft guns in the Spanish armed forces continued until the early 1970s.
By the beginning of World War II, there were 24 88-mm anti-aircraft guns in Greece. They engaged the Italian Air Force in 1940, and in April 1941 they fired on Luftwaffe aircraft. After the occupation of Greek territory, the surviving guns were used by the Nazis.
Anti-aircraft 88-mm guns of German production were in the armed forces of Bulgaria, Hungary and Romania. In the post-war period, the Flak 18/36 served in Bulgaria and Romania until the mid-1950s.
In 1943-1944, Finland purchased 90 8,8 cm FlaK 37 guns from Germany. The guns were supplied in two versions, the first batch included 18 anti-aircraft guns on a wheeled carriage, another 72 guns received in June 1944 were intended for installation on stationary concreted bases. Simultaneously with the first batch of Flak 37, the Germans provided 6 FuMG 62 Wurtzberg 39 fire control radars.
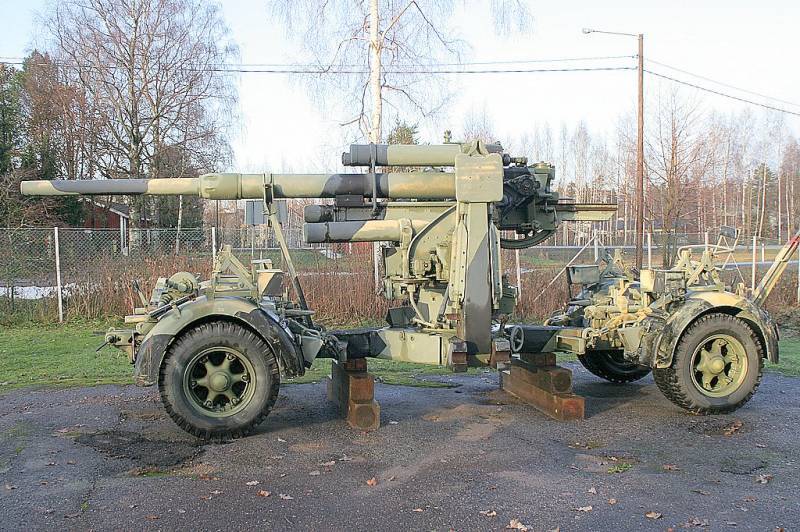

8,8 cm FlaK 37 at the Tuusula Anti-Aircraft Museum
FlaK 37 guns were used by the Finns as anti-aircraft guns until 1977, after which they were transferred to coastal defense. The Finnish army finally parted with 88-mm cannons at the beginning of the XNUMXst century.
After landing in Normandy, by mid-1944, the Americans captured more than 80 serviceable German 88-mm anti-aircraft guns. In the fall of 7, the 1944th and 79th artillery divisions were formed to use captured artillery as part of the US 244th Army.
These units were armed with 88-mm anti-aircraft guns, as well as 105 and 150-mm howitzers. By December 31, 1944, the 244th Field Artillery Division had fired a total of 10706 shots from captured German guns.
In March 1945, the newly formed French 401st and 403rd anti-aircraft artillery regiments were armed with captured German 88-mm cannons. Due to the lack of full-time German PUAZO, British GL Mk. II and GL Mk. III. German anti-aircraft guns remained in service with regular French units until 1953, after which they were used for training purposes for another 5 years.
In the post-war period, Yugoslavia, in addition to the guns recaptured from the Germans, received from various sources about 50 anti-aircraft guns 8,8 cm FlaK 18/36. The active service of the German anti-aircraft guns continued until the early 1970s, after which they were placed on the Adriatic coast as coastal artillery guns. After the collapse of Yugoslavia, German 88-mm anti-aircraft guns were used to fire at ground targets during the Serbo-Croatian armed conflict.
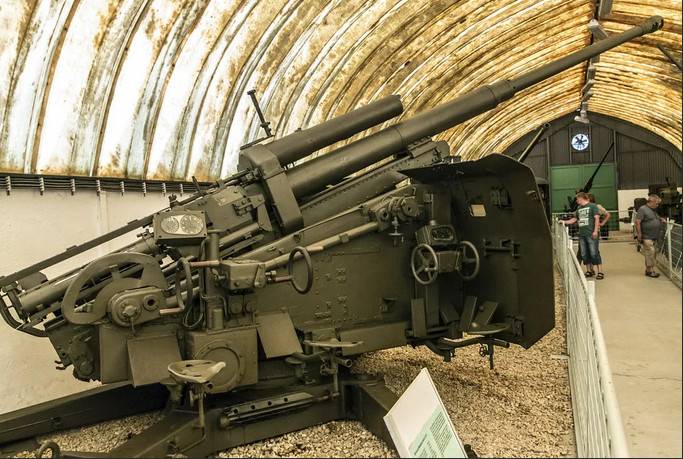

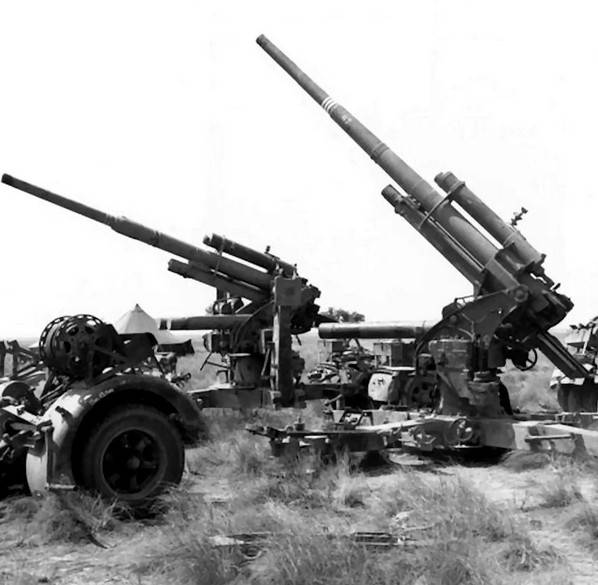
8,8 cm Flak 41 at the Leshany Military Technical Museum
Up to 300 anti-aircraft guns 8,8 cm Flak 18/36/37/41 after the end of World War II were at the disposal of the Czechoslovak army. Most of them in the early post-war years were offered to foreign buyers, but several batteries equipped with 8,8 cm Flak 41 continued to serve until 1963.
In the late 1950s, the Democratic Republic of Vietnam received several dozen 88-mm anti-aircraft guns from the Soviet Union. They took part in repelling the first raids of American aviation, but were later supplanted by 85 and 100-mm Soviet-made anti-aircraft guns.
The ending should ...





Information